In the previous post in this series, I wrote about two data warehouse systems that fit entirely in a 2U server, Fast Track-rated for 20TB to 28TB. In this blog post we’ll look at two more Fast Track systems, this time rated for 45TB to 55TB; one in a 2-socket, 2U server and the other in a 4-socket, 4U server.
Faster insights from your business data – that’s what you expect from your data warehouse to help you achieve your business outcomes, and SanDisk® enterprise flash makes it possible to deploy large data warehouse systems using storage that fits entirely within the server chassis. Let’s look at two such. These systems deliver very similar results, varying somewhat in capacity and performance.
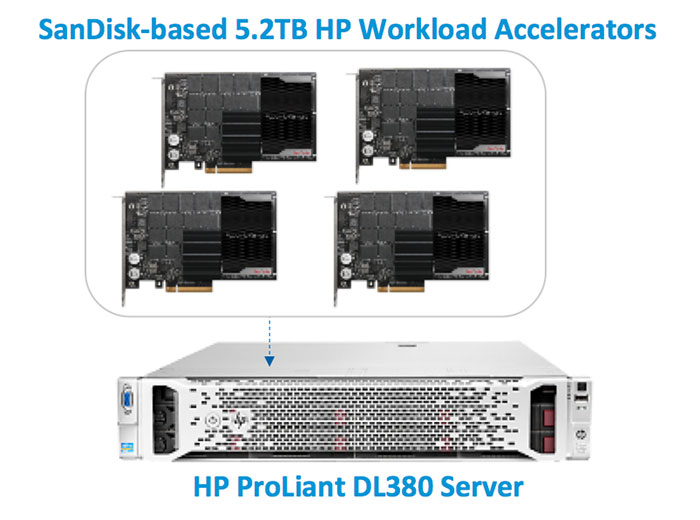
HP DL380 Gen8 server
The first system is based on the HP DL380 Gen8 server, FT-rated for a 45TB data warehouse. (Microsoft’s DWFT certification appears on page 7.) This is a 2-socket server that takes 2U of rack space.
This HP system stores the data warehouse on four HP 5.2TB FH/HL Light Endurance (LE) PCIe Workload Accelerators, which is HP’s rebranding of SanDisk Fusion ioMemory PX600-5200.
The “measured throughput” is 192 queries/hour/TB using SQL Server’s row store, or 1,476 queries/hour/TB using column store.
Those raw numbers, 192 and 1,476, are very similar to the 20-28TB systems, but remember, those are queries per terabyte per hour, so we get higher queries per hour from this system.
Multiplying queries by terabytes gives us 8,640 queries/hour using SQL Server’s row store features, and 66,420 queries/hour using SQL Server’s in-memory columnstore features. CPU utilization is 97% using row store, and 99% using columnstore.
Lenovo System x3850 X6
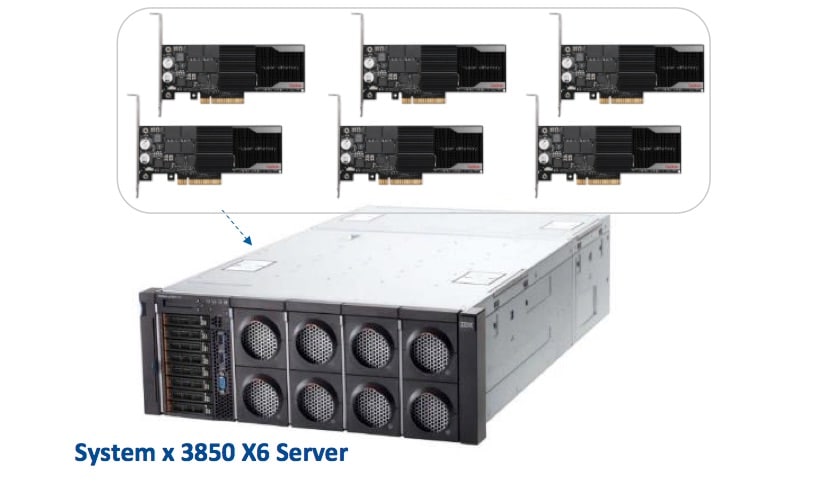
The second system is based on the Lenovo System x3850 X6, FT-rated for 55TB data warehouse. (Microsoft’s DWFT certification appears on page 4.) This is a 4-socket server that takes 4U of rack space. Lenovo classifies this as an Advanced data warehouse system with a capacity range of >40TB.
This system stores the data warehouse and tempdb on six IBM 3200GB Enterprise Value io3 Flash Adapter for System x, which is Lenovo’s branding of SanDisk Fusion ioMemory SX300-3200.
The “measured throughput” is 360 queries/hour/TB using SQL Server’s row store, or 2,538 queries/hour/TB using column store.
Multiplying queries by terabytes gives us 19,800 queries/hour using SQL Server’s row store features, and 139,590 queries/hour using SQL Server’s in-memory columnstore features. CPU utilization is 91% using row store, and 93% using columnstore.
Points of comparison
These two systems are substantially different: in physical size, processor and core count, number of ioMemory cards and their capacity.
The HP system uses four 5.2TB cards in a 2U server, with two 12-core processors for a total of 24 cores.
The Lenovo system uses six 3.2TB cards in a 4U server, with four 15-core processors for a total of 60 cores.
Both systems deliver high CPU utilization with 90%+ across the board.
The Lenovo system’s 36 additional cores and two additional controllers (on the 2 additional ioMemory cards) are why it delivers higher measured throughput (Queries/hour/TB).
What are the Benefits of These Systems?
Like the 20-28TB systems I referenced in my previous blog, these two systems also deliver similar, important benefits:
- Balanced. These systems are pre-configured and validated to be balanced data warehouse systems, avoiding the over- or under-spending in one area of the system; it’s just right for this capacity.
- Complete. These are complete solutions, ordered off the server vendors’ price lists. They include rebranded SanDisk flash, which is covered by the server vendor’s warranty and support services, and SQL Server 2014 Enterprise Edition for a complete set of business intelligence tools.
- Performance. The modern servers and CPUs take full advantage of the SanDisk flash storage to deliver the performance that lets benefit most from this data warehouse system. More users, more queries – more business insights, better business results.
- Simple and Compact. Everything you need is installed in a 2U or 4U server. No additional infrastructure is required to deal with external storage.
- Reliable and Economical. Using SanDisk flash instead of HDDs improves system reliability. SanDisk flash is significantly more reliable than HDDs with up to 10,000 times fewer uncorrectable bit errors, requires much less power to operate, and generates far less heat so you save on cooling cost.
Either of these systems is a great data warehouse solution for customers needing a 45-55TB data warehouse.
Learn more about data warehouse in the era of flash on our data warehouse hub, and at SQL PASS Summit – visit SanDisk in booth #222. I look forward to seeing you there!