5 Data Center Trends Driving the Next Generation of NVMe™ SSDs
Emerging technologies are dependent on massive data streams. With the announcement of two new families of NVMe SSDs, we take a look at the five key trends driving the next generation of solutions for data centers and cloud.
As the world of data evolves, so do applications and their storage needs. SSDs have become the de-facto choice for application acceleration. But they, too, are no longer a one-size fits all. We’re seeing new demands rising from workloads such as AI, machine learning and edge applications. Emerging technologies like autonomous driving, surveillance, and voice recognition are dependent on massive data streams, unimaginable just a few years ago. Data infrastructure is evolving to help organizations meet data demands and support new workloads and opportunities. As we look at the changing data landscape, there are 5 key trends driving the next generation of NVMe SSDs in data centers and the cloud:
1. Workload Evolution
Workloads are no longer just about traditional enterprise applications or databases. With the advent of cloud storage and the proliferation of analytics, edge devices and machine learning, IT organizations have to optimize their applications and infrastructure for new types of workloads. They must meet higher numbers of parallel users/streams (RIOPS), saturate their network (GB/s Read Bandwidth), meet data center and rack level power constraints with efficient power design (IOPS/Watt) and reduce the number of racks needed for storing more data than ever.
Furthermore, the diversity and type of data we’re seeing is changing. Video data is exploding. With 694K hours of video streamed by a major content provider in a single minute1 , VOD, streaming and caching videos have become the entertainment standard. Emerging technologies such as AI also rely heavily on video, image, and audio data streams.
2. A Better Understanding of the Role of Data Infrastructure
Whether it’s cloud-first companies, or organizations that are undergoing digital transformation, data center architects have a much deeper knowledge of their applications and what they demand of their infrastructure. With the need for efficiency at every layer of the stack, we particularly see a growing understanding of an application’s read and write patterns and the demand for an underlying storage device that can deliver the most optimal performance, endurance and power for the particular task.
3. Advancements in 3D NAND Technology
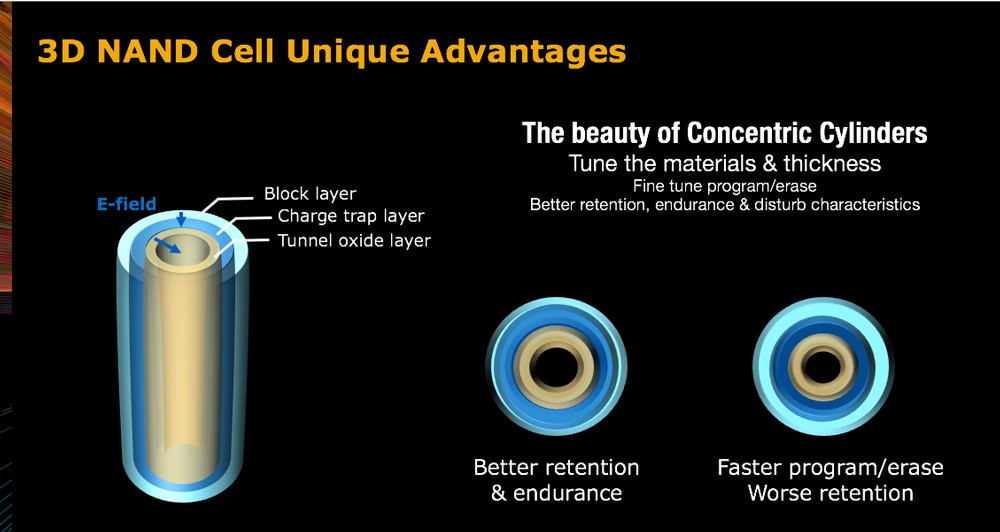
NAND technology has enabled the revolution of everything from IoT to mobile devices, personal computing, connected home, wearables, videography and flash in the data center. It is a technology that’s on an amazing trajectory as we’re able to architect more bits per die with every generation. Just last year we announced the world’s highest density monolithic 3D NAND chip. These advancements not only allow more capacity and higher density, they also enable new levels of performance and reliability, as we continue to drive down the cost per bit of storage. Furthermore, charged trapped device architecture allows us to tune 3D NAND cells for endurance, reliability and performance, opening up new possibilities for optimized flash-based devices.
4. NVMe
NVM Express (NVMe) is the first storage protocol designed to take advantage of high-performance flash storage media. It was designed from the ground up to take advantage of the low-latency of flash medium, and it is changing the game for data centers and applications, particularly for real-time analytics, machine-to-machine (M2M) workloads, Internet of Things (IoT), and emerging technologies like composable infrastructure that are based on NVMe Over Fabrics. We’re only scratching the surface of the impact NVMe will have on data infrastructure design over the next decade.
5. The Move from General to Purpose-Built Solutions
Data center customers that understand the nature of their data streams and application workloads are realizing that today’s general-purpose architectures are inefficient and can carry resource and cost overhead. This concept of “one size fits all” doesn’t work as the demand on data centers grows. Organizations need to have the ability to optimize solutions and adopt architectures that go beyond the limited resource ratios of general-purpose processing, memory, storage, and interconnect. With technologies like 3D NAND, and various tiers of flash enabled by NVMe and a growing diversity of form factors, optimized solutions will help deliver new efficiencies and capabilities that can meet the new demands of data.
Our Next Generation NVMe SSDs
This morning at Flash Memory Summit, we announced two new families of NVMe SSDs. Built on proven, vertically integrated in-house architectures, and 96L 3D TLC NAND, these new Ultrastar® NVMe SSDs set a new bar for performance and power efficiency, laying the foundation for next-generation purpose-built infrastructure.
Here’s a deeper dive into these solutions, and how current industry trends have helped shape their design.
Ultrastar DC SN640 – High Performance, Exceptional Flexibility and Powerful NVMe Features
The Ultrastar DC SN640 is purpose built to deliver high performance and advanced NVMe features across multiple form factors. We developed a fully vertically integrated SSD that utilizes our industry-leading 96-Layer BiCS4 NAND coupled with an advanced in-house NVMe controller that is optimized for low latency and power efficiency. This new family comes in three form factors with a broad range of capacity points, geared to support a variety of workloads:
- The EDSFF E1.L form factor offers up to 30.72TB, projected to deliver blazing speeds up to 720K random read IOPs and expected to be the highest performing E1.L. This game-changing form factor is ideal for designing best PB/rack for new dense data-center designs.
- U.2 7mm with up to 7.68TB, a popular form factor for storage servers, virtualized environments and containerized applications using denser, power-efficient blade systems.
- M.2 22×110 with up to 3.84TB for constrained spaces and OCP compliant hardware.
The Ultrastar DC SN640 is feature rich, supporting up to 128 NVMe namespaces, all mandatory commands in the NVMe Management Interface (NVMe-MI), and allowing firmware updates without a device reset. We know that software defined storage demands flexibility, so we’ve designed the DC SN640 with enhanced flexibility allowing a tradeoff of capacity for endurance, so you can tune it for the specific application being deployed.
Great use cases for its extreme performance in mixed-workload applications include SQL Server®, MySQL®, virtual desktops and other business critical workloads using hyperconverged Infrastructures such as VMware vSAN® and Microsoft Azure® Stack HCI solutions. You can learn more about our proven architecture, streamlined qualifications, and broad OS and hardware certifications in this product brief.
Ultrastar DC SN340 – High Bandwidth, Competitive Sequential Performance and Our Most Power Efficient SSD to Date
The Ultrastar DC SN340 Gen3 x4 PCIe SSD is optimized for power efficiency and low heat signature with less than 7W at full performance. Our innovative SSD controller design minimizes latency by incorporating hardware-based acceleration engines to deliver less than 500us read latencies in 99.99% of data requests, even at high queue depths.
With capacities of up to 7.68TB, we’ve design this SSD for very read-intensive workloads such as warm storage, and other applications that write in large blocks sizes. One such example is CDN and video caching, where data is written in large sequential blocks and can benefit significantly from the high-bandwidth of Gen3 x4 PCIe and low read latency of NVMe. Another great use case example is distributed No-SQL databases like Apache Cassandra® and MongoDB® that can also take advantage of the large-block write characteristics of the drive.
Utilizing PCIe Gen 3×4 interface the Ultrastar DC SN340 can reach speeds of up to 3.1GiB/s and 1.4GiB/s sequential read and write performance, this drive is built to accommodate technologies such as autonomous driving, surveillance, voice recognition and industries incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning. You can learn more in this product brief.
The Next Generation Data Center
The data center is undergoing tremendous changes. Organizations are rapidly transitioning to a variety of purpose-built solutions to improve performance, efficiency, density and overall TCO, and to enable new opportunities for data and revenue streams. The new Ultrastar NVMe SSDs are based on our deep understanding of evolving workloads and trends within the data center and NAND technology. We’re extremely proud that the new Ultrastar DC SN640 and DC SN340 SSDs are optimized to support purpose-built workloads and data volume demands of today, while laying the foundation for the future zettabyte scale.
Learn More
- Get to know our Ultrastar NVMe SSDs
- The Ultrastar DC SN640 product brief
- The Ultrastar DC SN340 product brief
1 https://www.visualcapitalist.com/what-happens-in-an-internet-minute-in-2019/
Forward-Looking Statements
Certain blog and other posts on this website may contain forward-looking statements, including statements relating to expectations for our product portfolio, the market for our products, product development efforts, and the capacities, capabilities and applications of our products. These forward-looking statements are subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed in the forward-looking statements, including development challenges or delays, supply chain and logistics issues, changes in markets, demand, global economic conditions and other risks and uncertainties listed in Western Digital Corporation’s most recent quarterly and annual reports filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission, to which your attention is directed. Readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements and we undertake no obligation to update these forward-looking statements to reflect subsequent events or circumstances.