ZNS SSDs Just Got Real – Ultrastar® DC ZN540 Now Sampling
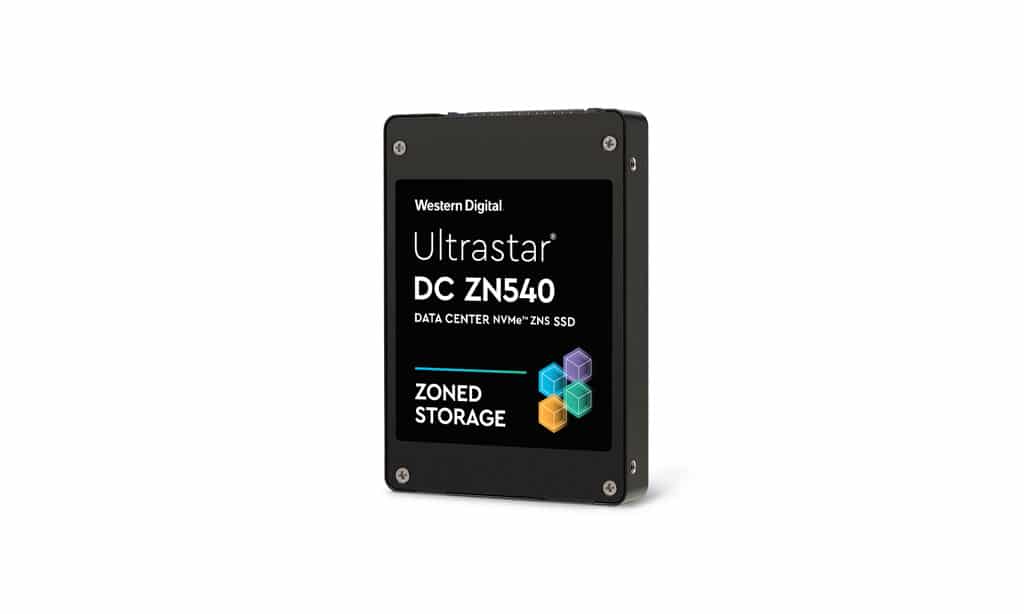
Western Digital, today, announced it is sampling a new generation of SSDs to select customers – Zoned Namespaces (ZNS) SSDs, specifically the Ultrastar DC ZN540 ZNS NVMe™ SSD. Here’s why ZNS SSDs are pivotal in the evolution of data-centric architectures as we enter the zettabyte era, and some real-world application testing results.

The advent of the cloud, analytics, AI and machine learning has made applications and system architectures extremely complex. Data infrastructures across the cloud, the edge, and billions of endpoint devices, are creating a meteoric growth in data and increasing complexity and degree of heterogeneity in the computing systems.
Designing systems to address the challenges described above, at this scale, actually expose and dilate any inefficiencies, such as utilization, performance inconsistencies, latencies/ QoS, and cost. ZNS SSDs are lean SSDs that are all about using storage devices in a more efficient way. They offer data-intensive, multi-tenant computing environments, new levels of performance (both throughput and latencies), better QoS, higher agility and efficiency at a lower TCO.
Next Generation Data Centers
Heterogeneous compute, human-machine and machine-machine interaction, and connected systems are going to generate a myriad of contextualized data as we draft the vision for the future data centers. The most pressing issue is to get the most value and reduce the cost of data storage and processing. The systems and data centers, and their technology partners, will need to continue to improve agility and resiliency, scale capacity, and utilization, all while reducing the TCO. Zoned Storage is an important and natural evolution in meeting some of these data center demands at-scale and delivering better performance and efficiencies consistently.
So, let’s talk about ZNS and how does it enable the Ultrastar DC ZN540 to deliver up to 4x throughput and 2.5x QoS improvements compared to conventional SSDs, what applications will see the best results and how can it lower data center TCO? Let’s get started.
Conventional vs. ZNS SSDs
Conventional SSDs are good at random I/O operations, but they have a finite lifetime based on program/erase cycles. As such, the two areas where the industry has been constantly innovating in SSD technology are improving performance and better endurance management. We have seen advancement in data placement within SSDs (with the help of the Flash Translation Layer and device DRAM), endurance management and background activities using SSD over provisioning. However, these in-device computational activities often lead to noisy neighbors, higher write and storage amplification, and throughput and QoS inconsistencies.
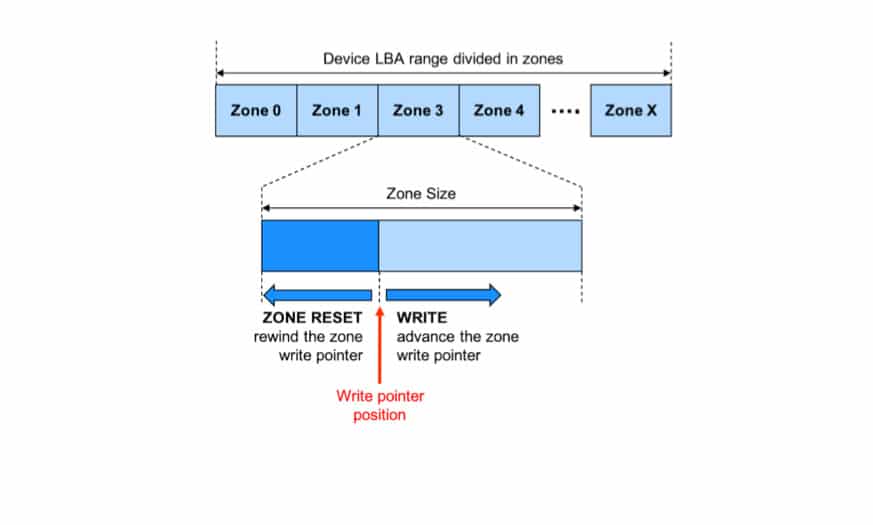
Zoned Storage is a concept applicable to both SMR HDDs and SSDs. These are drives with an address space, Logical block addressing (LBA), divided into zones, which have different I/O characteristics than that of conventional storage devices. The zones of zoned storage devices only write sequentially. Each zone has a write pointer that keeps track of the position of the next write. Data in a zone cannot be overwritten, it must first be erased using a special command (zone reset) – Figure #2.
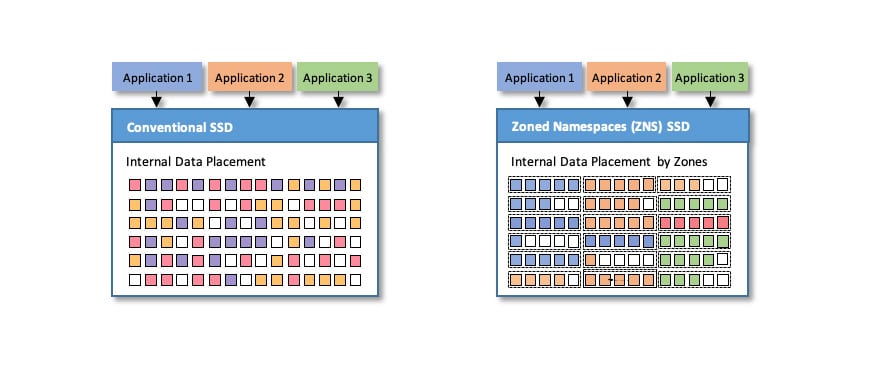
Why is this important? By shifting to selective data placement, small block random IOs to sequential data streams, and transferring data handling and management responsibilities from the device to the host, SSDs can reduce write/ storage amplification, lower onboard DRAM and NAND over provisioning, improve device throughput and latencies – Figure #3.
These fundamental architectural shifts enable, and will accelerate, the adoption of lower endurance media (QLC) in the public as well as private cloud infrastructures. For data center architects, these benefits lead to significantly lower data center TCO and improve system agility and utilization without much tradeoffs.
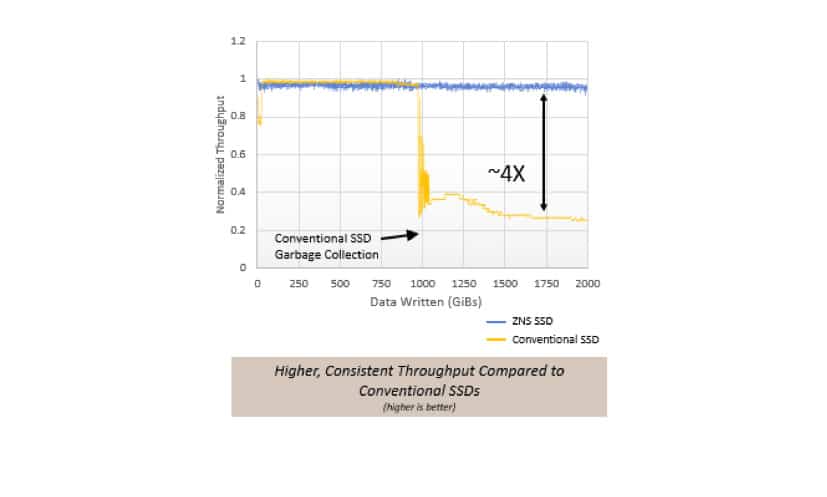
The Ultrastar DC ZN540 exhibits how by removing background activities, such as garbage collection, ZNS SSDs can offer up to 4x write bandwidth improvement – Figure #4. Besides significant throughput improvement, this also lowers system level TCO by replacing up to 4x conventional SSDs with 1x ZNS SSD, without any throughput reduction in a multi-tenant environment.
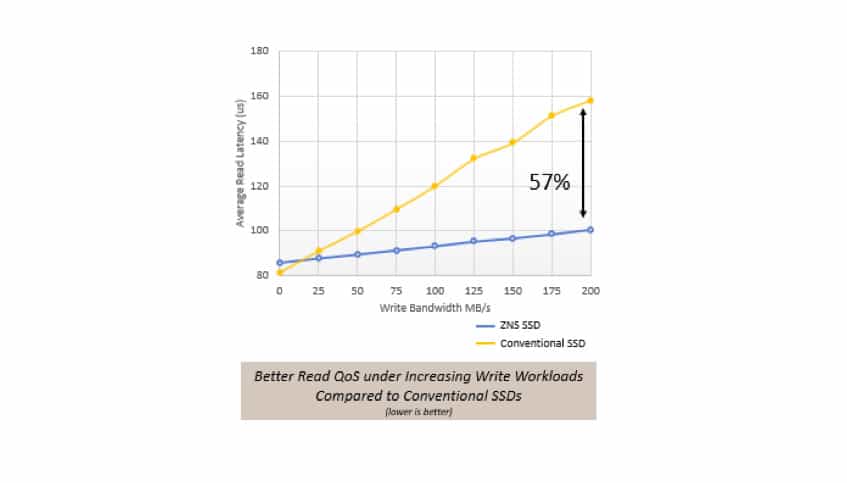
The HW-SW stack optimization with ZNS has also resulted in more than 57% latency and therefore QoS improvement. Once again, this also lowers system level TCO by replacing up to 4x conventional SSDs with 1x ZNS SSD in latency sensitive applications – Figure #5.
Application Testing
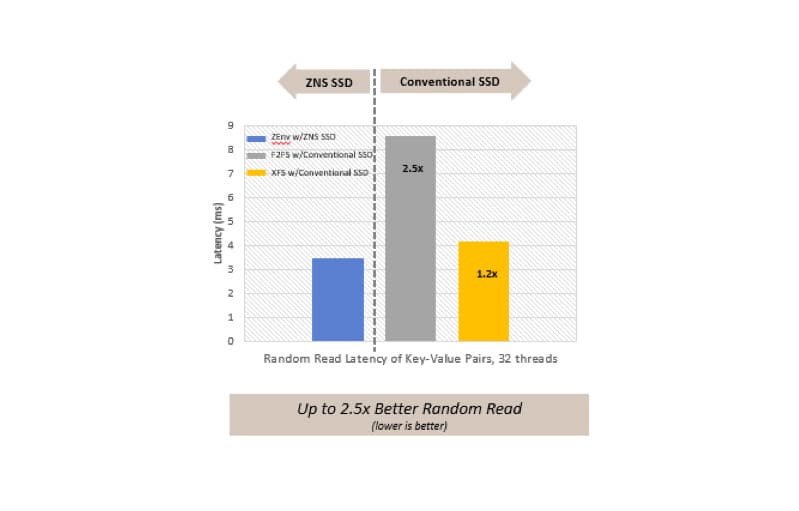
Next, Western Digital labs evaluated how ZNS drives perform in a real-world application environment such as RocksDB, a persistent key-value storage, running with LSM-Tree storage engine. The lab tests indicate that ZNS SSDs can deliver up to 2.5X lower latencies as compared to conventional drive with F2FS file system running 32 random read threads of key-value pairs – Figure #6.
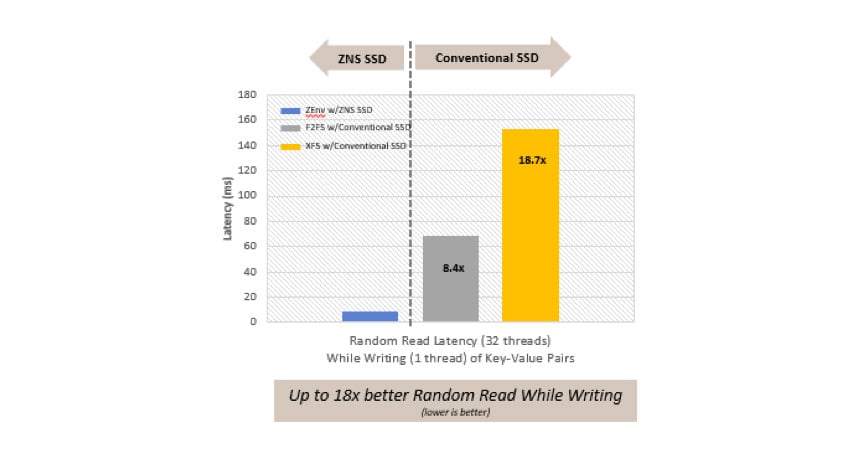
Furthermore, our lab tests also suggest that the ZNS SSDs can offer up to 18.7x lower latencies as compared to conventional drive with XFS file system running 32 random read threads and 1 write thread of key-value pairs- Figure #7.
These improvements are not, and should not be, limited to RocksDB only. There are several other databases, if ready to leverage LSM-Tree storage engine, can take advantage of ZNS SSDs. Western Digital is currently working on MySQL to show the similar benefits leveraging MyRocks translations.
Conclusion
Zoned Storage and ZNS SSDs are set to revolutionize storage and system architectures for next generation heterogeneous computing systems. The new architectures will expand the value of SSDs and include sequential data streams in applications such as persistent key-value storage for data, metadata, and machine learning training, inference and predictions. In addition, data centers are focusing on improving peak to average utilizations, achieving faster responses, preparing for future complex workload processing, and lowering TCOs. The Ultrastar DC ZN540 ZNS NVMe SSD is augmenting the evolution of next generation storage and system architectures by delivering higher throughput, better QoS and lowering the system TCO at-scale.
Get to know Zoned Storage at https://www.westerndigital.com/company/innovations/zoned-storage
* When compared to conventional SSDs